Simulating the SSH model#
Here we simulate the SSH model using the Pulser backend. We follow the work of De Léséleuc et al. in “Observation of a symmetry-protected topological phase of interacting bosons with Rydberg atoms” (available also on arxiv).
Using a Microwave channel, the interaction Hamiltonian is given by
where \(C_{ij} = \frac{C_3(1-3\cos^2\theta_{ij})}{R_{ij}^3}\). Here \(R_{ij}\) is the distance between qubits \(i\) and \(j\), \(R_{ij}=|\textbf{x}_i-\textbf{x}_j|\), and \(\theta_{ij}\) is the angle between \(\textbf{x}_i-\textbf{x}_j\) and the magnetic field. See the Pulser docs for more information.
By appropriate choice of the qubit geometry we can approximate the SSH model for hard bosons. For example, when $$ \theta_{ij} = \cos^{-1}\sqrt{1/3}$$ there will be no interaction between qubits \(i\) and \(j\). We use this to model the SSH model below.
import qse
import pulser
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
angle = np.arccos(np.sqrt(1.0 / 3.0)) * 180 / np.pi
print(f"Angle is: {angle:.2f} degrees")
Angle is: 54.74 degrees
We create two chains of qubits, A and B. By rotating them by the angle above, there will be no interactions between qubits on the same chain.
lattice_spacing = 12
repeats = 4
qbits1 = qse.lattices.chain(lattice_spacing=lattice_spacing, repeats=repeats)
qbits1.labels = [f"A{i}-{i}" for i in range(repeats)]
qbits2 = qse.lattices.chain(lattice_spacing=lattice_spacing, repeats=repeats)
qbits2.labels = [f"B{i}-{i+repeats}" for i in range(repeats)]
qbits2.translate((lattice_spacing * 0.5, 8, 0))
qbits_ssh = qbits1 + qbits2
qbits_ssh.rotate(
90 - angle
) # by rotating to this angle interactions in the A & B chains will cancel.
qbits_ssh.draw(show_labels=True, units="µm")
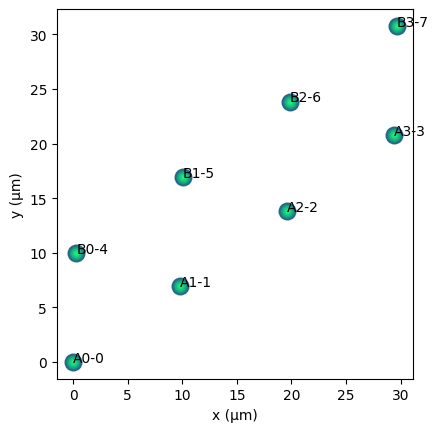
We can verify that there are no interactions in the same chain by computing the couplings between qubits.
magnetic_field = np.array([0.0, 1.0, 0.0])
c3 = 3700
def compute_hamilton_coef(i, j):
"""Compute the hamiltonian coefficient between qubits i & j."""
r = qbits_ssh.positions[i] - qbits_ssh.positions[j]
d = np.linalg.norm(r)
r /= d
cos_theta = np.dot(r, magnetic_field)
return c3 * (1 - 3 * cos_theta**2) / d**3
couplings = [
[compute_hamilton_coef(i, j) for j in range(i + 1, qbits_ssh.nqbits)]
for i in range(qbits_ssh.nqbits - 1)
]
couplings = [j for i in couplings for j in i]
coupling_mat = np.zeros((qbits_ssh.nqbits, qbits_ssh.nqbits))
coupling_mat[np.triu_indices(qbits_ssh.nqbits, 1)] = couplings
couplings
for i in range(1, qbits_ssh.nqbits):
print(f"Coupling between qbits 0 & {i}:", coupling_mat[0, i])
Coupling between qbits 0 & 1: -4.754427304529029e-16
Coupling between qbits 0 & 2: -5.943034130661286e-17
Coupling between qbits 0 & 3: 0.0
Coupling between qbits 0 & 4: -7.391286573549234
Coupling between qbits 0 & 5: -0.5880494737584242
Coupling between qbits 0 & 6: -0.09525640675644509
Coupling between qbits 0 & 7: -0.026269374219942052
# Let's visualize the couplings
bonds = np.abs(coupling_mat)
bonds /= np.max(bonds)
qbits_ssh.draw(show_labels=True, units="µm")
for i in range(0, qbits_ssh.nqbits - 1):
for j in range(i + 1, qbits_ssh.nqbits):
xs_ij = qbits_ssh.positions[[i, j]]
plt.plot(xs_ij[:, 0], xs_ij[:, 1], c="k", alpha=bonds[i, j], zorder=-1)
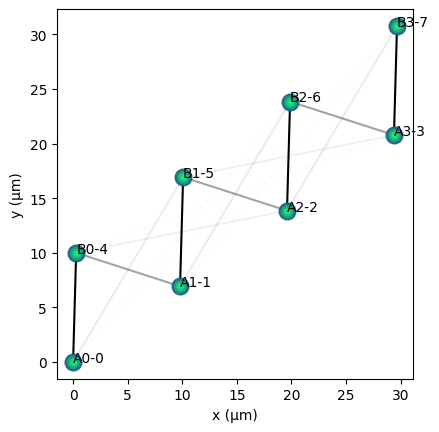
Thus we see that there are no couplings between qubits in the same chain, and hence we have a SSH model. Finally we can visualize the Hamiltonian.
simple_pulse = pulser.Pulse.ConstantPulse(10, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
pcalc_ssh = qse.calc.Pulser(
qbits=qbits_ssh,
amplitude=simple_pulse.amplitude,
detuning=simple_pulse.detuning,
channel="mw_global",
magnetic_field=magnetic_field,
)
pcalc_ssh.build_sequence()
pcalc_ssh.calculate()
10.0%. Run time: 0.00s. Est. time left: 00:00:00:00
20.0%. Run time: 0.00s. Est. time left: 00:00:00:00
30.0%. Run time: 0.00s. Est. time left: 00:00:00:00
40.0%. Run time: 0.00s. Est. time left: 00:00:00:00
50.0%. Run time: 0.00s. Est. time left: 00:00:00:00
60.0%. Run time: 0.00s. Est. time left: 00:00:00:00
70.0%. Run time: 0.00s. Est. time left: 00:00:00:00
80.0%. Run time: 0.00s. Est. time left: 00:00:00:00
90.0%. Run time: 0.00s. Est. time left: 00:00:00:00
100.0%. Run time: 0.01s. Est. time left: 00:00:00:00
Total run time: 0.01s
time in compute and simulation = 0.06736326217651367 s.
ham = pcalc_ssh.sim.get_hamiltonian(0).full()
fig = qse.visualise.view_matrix(ham.real, vcenter=0.0)
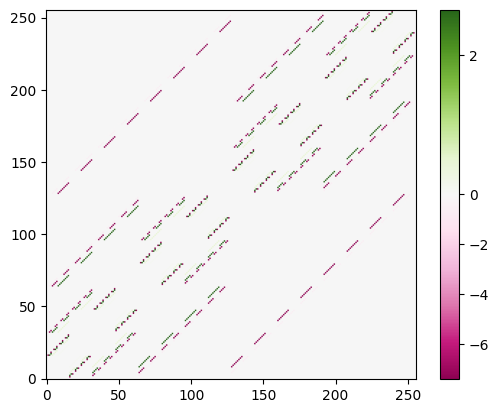
Version#
qse.utils.print_environment()
Python version: 3.12.12
qse version: 1.0.3